Service Registry and Discovery Pattern
Introduction
Microservices are transforming the way applications are developed and deployed. In a microservices architecture, applications are composed of small, independent services that communicate over a network. The Service Registry and Discovery Pattern plays a crucial role in managing this communication, making the entire system more resilient and scalable.
Importance of Service Registry and Discovery
Service Registry and Discovery offers several essential benefits:
-
Dynamic Scaling: Allows services to be easily scaled up or down as needed.
-
Load Balancing: Ensures that requests are distributed evenly across multiple instances of a service.
-
Fault Tolerance: Continues to route requests to available instances if one or more fail.
-
Enhanced Collaboration: Enables different services to discover and communicate with each other seamlessly.
What's the Problem/Challenge?
The following challenges are addressed by the Service Registry and Discovery Pattern:
-
Dynamic Nature of Services: Microservices can be dynamically scaled, requiring constant tracking of instances and locations. Manual tracking can become complex and error-prone.
-
Failure Handling: Without a proper registry and discovery mechanism, failed services can remain undetected, leading to system delays and failures.
-
Complexity in Communication: As the number of microservices increases, communication becomes more complex. Identifying the right service and routing requests requires automation.
-
Load Balancing Issues: Implementing efficient load balancing without service discovery can be challenging and tedious.
-
Lack of Agility: Without a systematic approach, agility can be lost, affecting system responsiveness.
-
Security Concerns: Unauthorized access to service instances can be a risk. A service registry provides centralized management and monitoring.
Key Components
1. Service Discovery
-
Client-Side Discovery:Clients query the registry and decide which service to call, providing more control but increased complexity.
-
Server-Side Discovery:A load balancer queries the registry and routes the request, simplifying the client but potentially adding latency.
2. Service Registry
-
Registration: Services register themselves upon startup, providing details like location, IP, and port.
-
Deregistration: Services are removed from the registry when they shut down, ensuring that requests are not sent to non-functioning instances.
-
Health Check: Regular checks ensure that service instances are available and healthy.
Server-Side Service Discovery
 Image credits to nginx
Image credits to nginx
How It Works
-
Client Requests: The client sends a request to a load balancer.
-
Querying the Registry: The load balancer finds available instances.
-
Selecting an Instance: The load balancer selects an instance.
-
Forwarding the Request: The request is sent to the selected instance.
Advantages
-
Simplified Clients: Clients only need to know the load balancer’s address.
-
Consistent Behavior: Ensures uniform load balancing and failure handling.
Drawbacks
-
Additional Latency: May add network latency.
-
Single Point of Failure: If the load balancer fails, it affects the system.
Implementing Service Registry and Discovery
Various tools and platforms can implement this pattern:
-
Eureka: An open-source tool from Netflix, often used with Spring Boot.
-
Consul: A multi-platform tool providing both registry and discovery.
-
Zookeeper: A distributed coordination service used for registry and discovery.
Client-Side Service Discovery
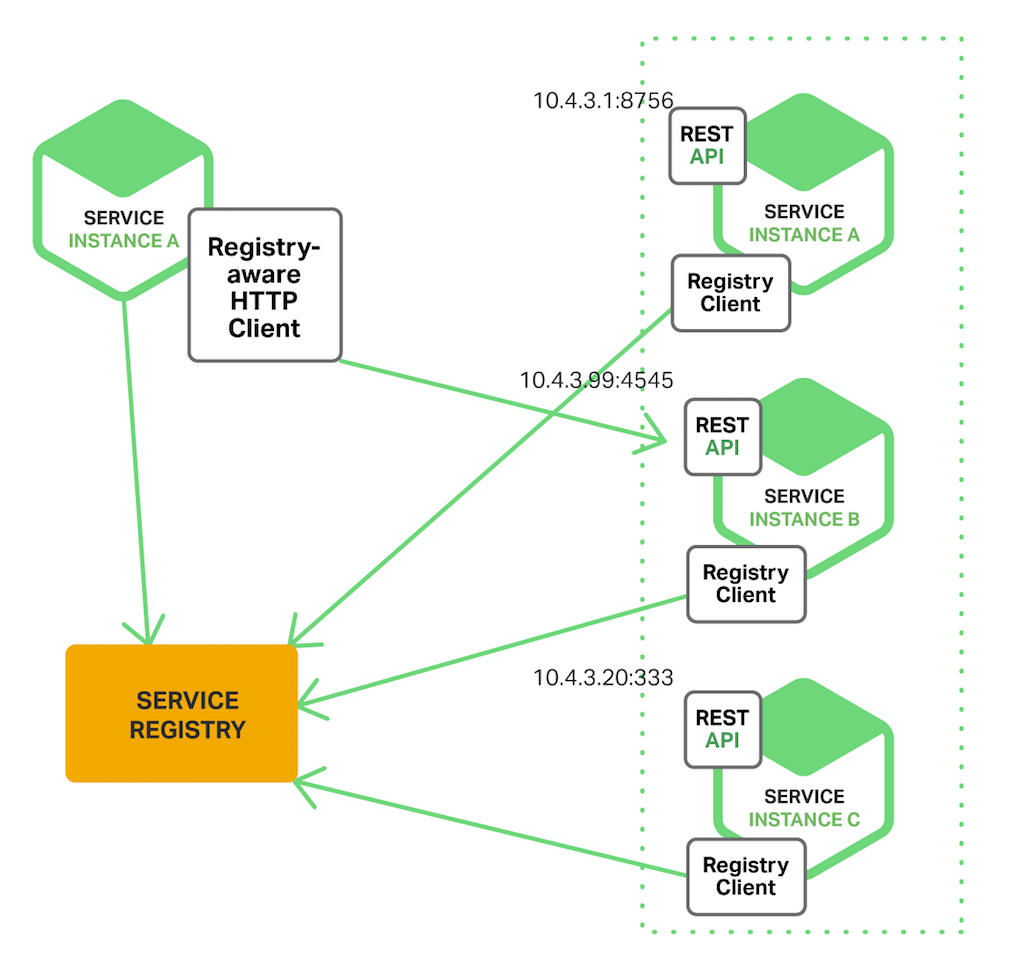 Image credits to nginx
Image credits to nginx
How It Works
-
Querying the Registry: The client obtains available instances.
-
Selecting an Instance: The client uses load balancing to select an instance.
-
Making a Request: The client requests the chosen instance directly.
Advantages
-
Flexibility: More control over load balancing.
-
Reduced Latency: Direct communication can reduce network latency.
Drawbacks
-
Complexity: Increased client management.
-
Inconsistency: Different clients may have inconsistent strategies.
Conclusion
The Service Registry and Discovery Pattern is vital in modern microservices architecture. By providing a systematic way to manage the dynamic nature of microservices, it ensures robustness, agility, and efficiency. Choosing between Client-Side and Server-Side depends on specific requirements and often involves a balanced combination of both.
