Understanding the SSL Handshake in HTTPS
Introduction
The Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) handshake is a vital component of modern online security. In today's increasingly digital world, understanding how your data is protected is crucial. This blog post will explore the SSL handshake process in HTTPS, breaking down its complexity into easy-to-understand segments.
What Are SSL and HTTPS?
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer)
SSL is a cryptographic protocol designed to provide secure communication over a computer network. It encrypts the data sent between two systems, ensuring privacy and data integrity.
HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure)
HTTPS leverages SSL to encrypt the HTTP protocol, protecting data transferred over the web. When browsing a website with HTTPS, all communication between your browser and the server is secure and encrypted.
The SSL Handshake: A Step-by-Step Guide
What is SSL Handshake?
The SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) handshake is a protocol that establishes a secure encrypted connection between a client (such as a web browser) and a server (web server). This handshake ensures that the data exchanged between the client and server remains confidential and tamper-proof. Let's break down the SSL handshake process into several key steps:
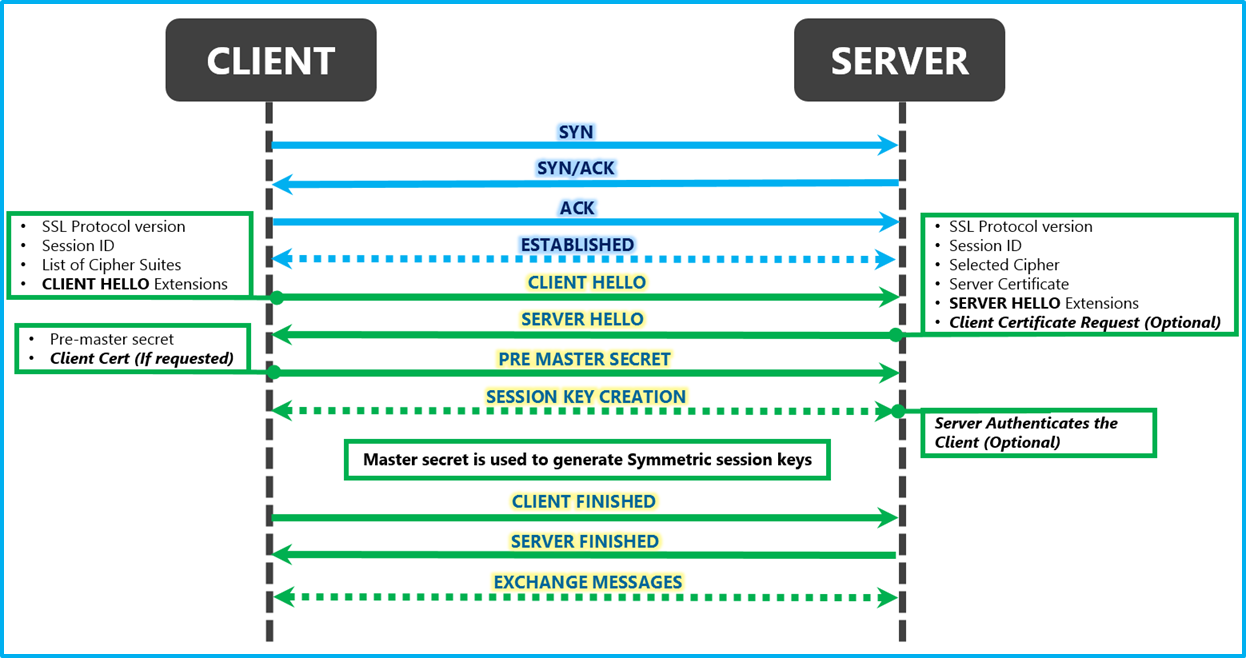 Image credits to medium
Image credits to medium
1. ClientHello
Supported Cryptographic Algorithms
The client sends a list of supported cryptographic algorithms, session settings, and a random value, signaling the start of the handshake process.
Session ID
If resuming a previous session, the client sends the session ID to speed up the process.
2. ServerHello
Server's Response
The server picks the cryptographic algorithms from the client's list that it also supports.
Server's Certificate
The server then sends its SSL certificate, allowing the client to verify its identity.
Key Exchange Method
The server selects the key exchange method suitable for both parties.
3. Client's Authentication
Verification of Server's Certificate
The client checks the server's certificate with the Certificate Authority (CA) to ensure its legitimacy.
Pre-Master Secret
The client generates and sends an encrypted pre-master secret using the server's public key.
4. Finalizing the Handshake
Generating Master Secret
Both parties use the pre-master secret to generate a master secret, forming the foundation of their secure connection.
Session Keys Creation
The master secret is then used to create session keys for encrypting and decrypting information.
Finished Messages
Both sides send encrypted "finished" messages, marking the successful completion of the handshake.
Why Is the SSL Handshake Important?
Understanding the SSL handshake provides insight into the security mechanisms that protect our online communications. By ensuring that both parties are who they claim to be and encrypting the data transferred between them, the SSL handshake maintains privacy and data integrity in our digital world.
Conclusion
The SSL handshake is more than a complex technical process; it's a vital component of online security. As internet users and developers, understanding how the SSL handshake works allows us to appreciate the robust protections that keep our online interactions safe.
